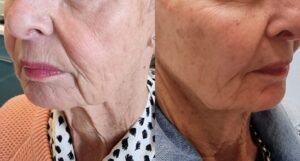
I. Background knowledge
Hyaluronic acid (HA), also known as hyaluronic acid, is a transparent acidic mucopolysaccharide. In 1934, Meyer, a professor of ophthalmology at Columbia University in the United States, first isolated the substance from the vitreous body of bovine eyes and analyzed its structure.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) first approved bovine collagen for skin fillers in 1981. In 2003, hyaluronic acid injection beauty products were launched on the market, growing rapidly at a rate of nearly 25% per year, becoming the second largest injection beauty product after botulinum toxin.
In December 2008, the State Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) approved the Swedish Q-Med company’s hyaluronic acid skin filler “Restylane” to be launched in China. Hyaluronic acid belongs to the category of human implants in CFDA approval and must be included in the management and declaration of medical devices. At present, the imported hyaluronic acid approved for listing in my country includes: Juvederm, Restylane 2, Iwan and Ailiwei, etc.; domestic products such as Yimei, Runbaiyan, Bonida, Haiwei, Shuyan, Fasili, Aifulai and Xinfeiling.
Ordinary hyaluronic acid will be metabolized into CO2 and water in the body within 1 to 2 days. When used as a skin filler, a cross-linking method (i.e. cross-linked hyaluronic acid) is used to delay its degradation rate and prolong the efficacy. Cross-linking technology can increase the size of hyaluronic acid particles. The larger the particles, the slower the degradation rate. They maintain the effect for about 6 to 9 months, and the efficacy of some products can be maintained for 1 to 2 years.
2. Specific applications
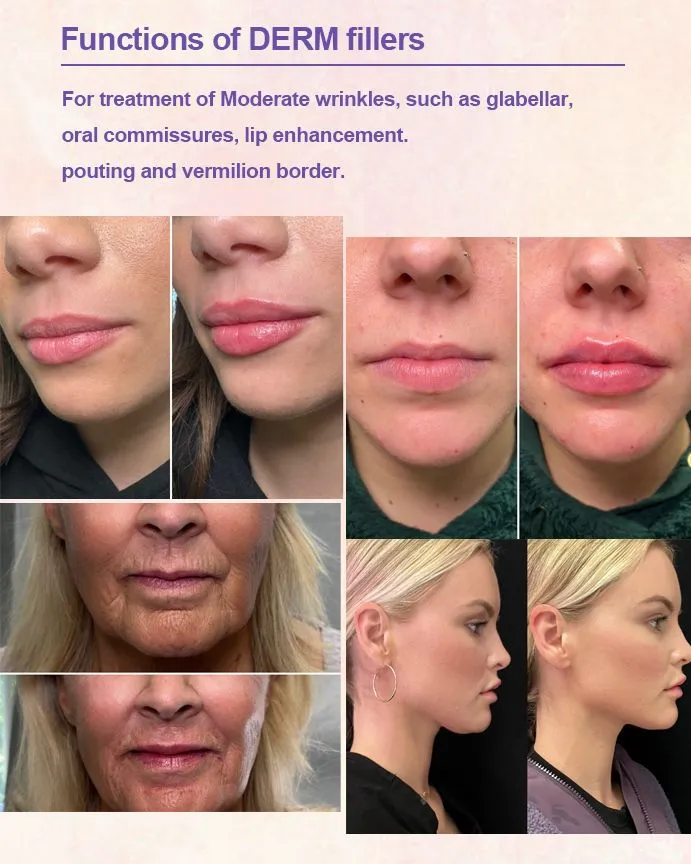
1. Filling wrinkles
Hyaluronic acid injected into the dermis can effectively solve a variety of wrinkles, especially for static wrinkles. Such as frown lines, crow’s feet, tear grooves and nasolabial folds.
2. Filling the lips
The lips will shrink with age, and the corners of the mouth will also sag due to aging. Therefore, the perioral area is another common site for filling injection treatment. Hyaluronic acid filling material is injected into the lips to support the sunken lips by increasing the volume of subcutaneous tissue, changing the shape of the lips, making the lips fuller and lifting the corners of the mouth.
3. Filling the face
Filling the face to make up for the lack of subcutaneous fat and muscle, improve the facial contour, such as cheek depression, facial asymmetry, depression under the zygomatic arch, flat temporal area, significant depression of the temple, or too flat facial contour, lack of three-dimensional sense, etc., to create an ideal appearance for the face.
4. Rhinoplasty
By filling the subcutaneous tissue of the nose with hyaluronic acid, the effects of raising the bridge of the nose, repairing the tip of the nose, etc. can be achieved, and the poor nose shape can be improved. It is suitable for low nose, saddle nose, wavy nose, drooping nose tip, low root of the nose, etc. It can also be used to treat patients with poor results after rhinoplasty, and to trim local areas to avoid the risk of secondary rhinoplasty.
5. Filling dents
Injecting hyaluronic acid can not only increase the volume of subcutaneous tissue, but also stimulate collagen synthesis. Injection filling technology is increasingly used in some diseases such as acne and chickenpox, skin atrophy scars caused by trauma, infection, surgery, and soft tissue atrophy caused by congenital factors.
6. Breast augmentation and buttocks lift
Use larger particles of hyaluronic acid dermal fillers to inject into women’s breasts or buttocks to make the breasts or buttocks fuller. This method has the advantages of small wounds, light impact on the body, and real feel after treatment, but some scholars believe that it may affect the diagnosis of breast cancer.
7. Fat atrophy
Facial fat atrophy is a common side effect of antiviral treatment in AIDS patients, with the most obvious depression in the temporal and infraorbital areas. Studies have shown that large-particle hyaluronic acid can be used as a long-lasting and well-tolerated skin filler for AIDS patients with facial fat atrophy.
3. Adverse reactions and prevention and treatment
1. Injection reaction is the most common adverse reaction of hyaluronic acid filling, such as bleeding at the injection site, mild swelling, bruises and pain;
Prevention and treatment methods: Try to use a small sharp needle and change the needle after injecting 4 to 5 points. Slow injection can reduce the pain during puncture and injection. To reduce the probability of bleeding and bruising, patients should suspend immunomodulators and anticoagulants, and (or) drug supplements with anticoagulant activity 2 weeks before injection
2. Allergic reactions (including immediate and delayed). Although the antigenicity of hyaluronic acid itself is very low, some hyaluronic acid fillers contain lidocaine. If the patient is allergic to lidocaine, cross-linking agents, and foreign body structures of cross-linked hyaluronic acid, allergic reactions will occur;
Prevention and treatment methods: If allergic symptoms occur, oral antihistamines or glucocorticoids and corresponding topical medications can be used for treatment. For those with recurrent attacks, hyaluronidase can be used for dissolution.
3. Infection. Risks come from the activation of endogenous pathogens (such as herpes virus) or invasion of external pathogens (such as bacteria and fungi), as well as biofilm formation and vascular embolism leading to secondary infection of skin blood supply disorder;
Prevention and treatment methods: divided into early acute infection and delayed chronic infection. Early acute infection occurring within 2 weeks after injection should be treated with antibiotics in time. Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium (375 mg each time, once every 8 hours, 7 to 10 days of treatment) is recommended. Those who are allergic to penicillin can choose clindamycin (150 mg each time, once every 6 hours, 7 to 10 days of treatment). Delayed chronic infection occurring 2 weeks after injection should also be treated with antibiotics first. It is recommended to use third-generation or fourth-generation cephalosporins.
4. Tyndall phenomenon: injecting more hyaluronic acid or injecting shallowly in thin skin areas will cause the local skin to appear blue under light;
Prevention and treatment methods: Filling should follow the principle of “better deep than shallow, better less than more”. Too shallow is easy to form Tyndall phenomenon, which can be improved by pressing the periphery or injecting hyaluronidase to dissolve.
5. Nodules and cord-like protrusions are caused by excessive total injection or too shallow injection layer;
Prevention and treatment methods: massage and hyaluronic acid dissolution can be used. Hyaluronidase can be used for deeper nodules.
6. Granuloma reaction, caused by type IV allergic reaction caused by foreign bodies, is generally a delayed type, often appearing several months or even years after injection. Different from the nodules formed immediately after injection, these granulomas often do not have typical inflammatory reactions such as redness, swelling, heat and pain at the beginning, and only occur at the injection site. The probability of granulomas after hyaluronic acid filling is about 0.04%~0.40%;
Prevention and treatment methods: Some patients relapse without treatment within 1 year. The treatment method is local injection of corticosteroids. If the injection treatment is ineffective, surgical resection can be performed, but usually these granulomas have unclear boundaries with normal tissues and are prone to recurrence.
7. Vascular embolism is a serious adverse reaction of hyaluronic acid filling. Common embolism sites are superficial blood vessels on the face, but embolism of the ophthalmic artery and its branches, or even intracranial arteries, can also occur, which can lead to tissue necrosis, blindness, and even life-threatening;
Prevention and treatment methods: First, doctors need to be familiar with the anatomical structure of the injection site and possible individual variations; inject slowly with the smallest possible thrust, choose a thin needle to reduce the amount of injection, the injection volume at the same location should not be too large, and use a blunt needle to avoid direct puncture of the blood vessel.
8. Others, such as shallow and fast injections that block blood flow in the dermal vascular network can cause skin whitening, too deep injections cause insufficient filling, and delayed inflammatory reactions such as capillary dilation after injection, redness, swelling, and paresthesia caused by local irritation.
IV. Summary
Inexperience is the main factor for adverse reactions, and clinicians should choose appropriate products and use the right techniques to reduce adverse reactions. Clinicians should have a comprehensive understanding of the anatomical structure related to the injection site, and understand the patient’s entire history of previous cosmetic surgeries before treatment to determine whether there are absolute or relative contraindications. The correct choice of blunt or sharp needles can safely and effectively inject hyaluronic acid fillers. In areas prone to vascular-related adverse reactions, the expert group recommends that sharp needle injections be used with caution, as blunt needle injections are safer in these areas.
https://www.linkedin.com/company/dermyouth-beauty-skin-co-ltd/?viewAsMember=true